Can Inflammation cause Weight gain: Strategies and Tips Inflammation is a natural response of the body to protect itself from harm. It plays a crucial role in the immune system, helping to fight off infections and repair damaged tissues.
However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to a variety of health problems, including weight gain. This article explores the relationship between inflammation and weight gain, the mechanisms behind it, and how to manage inflammation for weight control.
Understanding Inflammation and its Impact on Weight

- Recognize Signs of Inflammation: Be aware of symptoms such as chronic fatigue, joint pain, digestive issues, and unexplained weight gain, as these could indicate underlying inflammation.
- Learn About Inflammatory Foods: Educate yourself on foods that can trigger inflammation, such as processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats, to make informed dietary choices.
- Embrace Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Incorporate more anti-inflammatory foods into your diet, including fruits, vegetables, fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and herbs like turmeric and ginger.
- Opt for Whole Foods: Choose whole, unprocessed foods over packaged and processed options, as they tend to be lower in inflammatory ingredients like added sugars and trans fats.
- Watch Your Sugar Intake: Limit your consumption of sugary drinks, sweets, and desserts, as excess sugar can contribute to inflammation and weight gain.

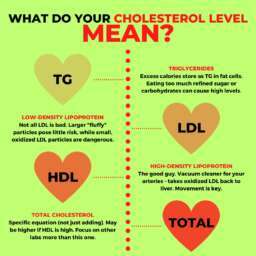
The Relationship Between Inflammation and Weight Gain
| INFLAMMATION | WEIGHT GAIN |
|---|---|
| Chronic inflammation is associated with oxidative stress | Oxidative stress can lead to weight gain and metabolic disturbances |
| Inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-18) promote adipose tissue inflammation | Adipose tissue inflammation can impair insulin sensitivity |
| Increased production of leptin, a hormone involved in appetite regulation | Leptin resistance can develop, leading to overeating and weight gain |
| Activation of inflammatory pathways in adipose tissue | Contributes to adipocyte dysfunction and obesity |
| Elevated levels of inflammatory molecules disrupt lipid metabolism | Impairs the breakdown and storage of fats |
| Chronic inflammation can induce insulin resistance in skeletal muscle | Impedes glucose uptake and utilization, leading to elevated blood sugar levels |
| Interference with adiponectin production, a hormone with anti-inflammatory properties | Reduced adiponectin levels are associated with increased risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome |
| Chronic low-grade inflammation may disrupt hypothalamic signaling pathways | Leads to dysregulation of appetite and energy expenditure |
Understanding the intricate interplay between inflammation and weight gain is essential for developing effective interventions aimed at addressing both inflammation and obesity.

Mechanisms Behind Inflammation-Induced Weight Gain
- Hormonal Dysregulation: Chronic inflammation disrupts the balance of hormones involved in appetite regulation and metabolism. Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), can interfere with the function of leptin, a hormone that signals satiety, leading to overeating and weight gain.
- Insulin Resistance: Inflammation can induce insulin resistance, impairing the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Insulin resistance promotes the storage of excess glucose as fat, leading to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen.
- Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines can trigger inflammation within adipose tissue, leading to adipocyte dysfunction. Dysfunctional adipocytes are less efficient at storing and releasing energy, contributing to metabolic disturbances and weight gain.
- Altered Lipid Metabolism: Chronic inflammation disrupts lipid metabolism, impairing the breakdown and storage of fats. This can lead to an imbalance between fat storage and utilization, resulting in increased fat accumulation and weight gain.
- Gut Microbiota Imbalance: Inflammation can alter the composition and function of the gut microbiota, leading to dysbiosis. Imbalanced gut microbiota are associated with increased inflammation and metabolic dysfunction, contributing to weight gain and obesity.
Can Inflammation cause Weight Gain
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Inflammation and Weight Gain
- Poor Dietary Choices: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats can promote inflammation in the body. These dietary choices can also lead to weight gain due to their high calorie content and low nutritional value.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is associated with increased inflammation and weight gain. Regular exercise helps reduce inflammation by promoting circulation, improving insulin sensitivity, and supporting metabolic health.
- Chronic Stress: Chronic stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can promote inflammation and contribute to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen. Stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help mitigate the effects of stress on inflammation and weight.
- Inadequate Sleep: Poor sleep quality or insufficient sleep duration can increase inflammation and disrupt hormonal balance, leading to weight gain. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption can promote inflammation in the body and contribute to weight gain due to its high calorie content. Limiting alcohol intake and opting for healthier alternatives can help reduce inflammation and support weight management.
Can Inflammation cause Weight Gain
Managing Inflammation for Weight Control
- Follow an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Base your meals on whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber to help reduce inflammation.
- Limit Inflammatory Foods: Minimize or avoid foods that can trigger inflammation, such as processed foods, refined sugars and excessive alcohol. These foods can promote inflammation and contribute to weight gain.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out toxins and reduce inflammation. Hydration is essential for overall health and can support weight control efforts.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Incorporate regular exercise into your routine to help reduce inflammation and support weight management. Aim for a combination of cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises for optimal results.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature. Chronic stress can promote inflammation and contribute to weight gain, so it’s essential to find healthy ways to manage stress.
Can Inflammation cause Weight Gain
How to Lose Inflammation Weight Fast?
To lose inflammation related weight quickly, it’s essential to focus on reducing inflammation in the body while also making healthy lifestyle choices. Here are some tips to help you lose inflammation weight fast:
- Follow an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Base your meals on whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid or minimize foods that can trigger inflammation, such as processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats.
- Increase Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, into your diet. Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body.
- Limit Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates: Cut back on sugary drinks, sweets, and foods made with refined flour. These foods can spike blood sugar levels and contribute to inflammation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out toxins and reduce inflammation. Herbal teas and infused water can also be beneficial.
- Include Anti-Inflammatory Herbs and Spices: Incorporate herbs and spices like turmeric, ginger, garlic, and cinnamon into your meals. These ingredients have natural anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Can Inflammation cause Weight Gain
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can inflammation cause weight gain?
A: Yes, chronic inflammation can disrupt hormonal balance and metabolic function, leading to weight gain.
Q: How can I tell if inflammation is causing my weight gain?
A: Symptoms of chronic inflammation include fatigue, joint pain, digestive issues, and unexplained weight gain.
Q: What foods should I eat to reduce inflammation and lose weight?
A: Foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber can help reduce inflammation and promote weight loss.
Q: Are there any supplements that can help reduce inflammation and promote weight loss?
A: Supplements such as fish oil, turmeric, and probiotics may help reduce inflammation. But it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking them.
Q: Can exercise reduce inflammation and aid in weight loss?
A: Yes. Regular exercise has been shown to reduce inflammation and promote weight loss by improving metabolic function and reducing fat mass.
Can Inflammation cause Weight Gain
Conclusion
In conclusion, chronic inflammation can contribute to weight gain and obesity by disrupting hormonal balance, metabolic function, and appetite regulation. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques. This is essential for managing inflammation and promoting weight loss. By understanding the relationship between inflammation and weight gain and taking proactive steps to reduce inflammation. Individuals can improve their overall health and well-being.